When you're diving into the world of home loans, you'll hear a lot of acronyms and jargon thrown around. One of the most important is the Loan-to-Value ratio, or LTV.
So, what is it? Simply put, the LTV ratio is a percentage that shows how much of a home's price you're borrowing compared to its actual appraised value. It's the lender's quick way to see how much skin you have in the game versus how much they're being asked to put up.
What Does Loan to Value Ratio Mean?

Imagine your home purchase is a bit like a seesaw. The loan amount you need is on one side, and the home's total value sits on the other. The LTV ratio is just a measure of the balance between the two. For lenders like Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage), this percentage is one of the first things they look at. It gives them a clear, immediate snapshot of the risk involved with your mortgage.
A high LTV means you're borrowing most of the home's value and making a smaller down payment. Lenders see this as higher risk. On the flip side, a low LTV means you're putting down a hefty sum of your own money, which makes the loan less risky for the lender. This one number can genuinely shape your entire homebuying experience.
The Role of LTV in Lending
Lenders use the LTV ratio as a fundamental tool to gauge their potential financial exposure. If a borrower defaults on a loan with a high LTV, there's a much smaller equity cushion for the lender to recover their money if they have to sell the property. For instance, a 97% LTV means you, the borrower, only have 3% equity in the home from the get-go.
This risk assessment has a direct impact on several key parts of your mortgage:
- Interest Rates: A lower LTV often gets you better interest rates because your loan is considered safer.
- Loan Approval: Some mortgage programs have very specific LTV limits. If you're over that limit, you might not get approved.
- Mortgage Insurance: With most conventional loans, if your LTV is above 80%, you'll be required to pay Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)—an extra monthly cost designed to protect the lender.
The loan-to-value ratio is a common term used by finance professionals to describe the ratio between a loan and the value of the asset. A lower LTV demonstrates a stronger financial commitment from the borrower, making the loan application more appealing.
A Quick Glance at High vs Low LTV
Getting a handle on the difference between high and low LTV helps make it clear why lenders care so much about this number. Let's break down what each scenario typically means. For a more detailed look, you can learn more about how Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage) evaluates loan to value ratios on our website.
Here's a quick summary table to show what these different LTV scenarios mean for both the lender and the homebuyer.
Loan to Value At a Glance
| LTV Scenario | What It Means for the Lender | Impact on the Borrower |
|---|---|---|
| High LTV (e.g., 95%) | Increased financial risk due to a smaller equity buffer. | Requires a smaller down payment but often leads to higher interest rates and mandatory mortgage insurance. |
| Low LTV (e.g., 80%) | Reduced financial risk with a significant equity cushion. | Requires a larger down payment but typically results in better interest rates and no PMI. |
At the end of the day, this percentage really sets the stage for your loan terms. A solid grasp of what it means gives you the power to make smarter decisions as you get ready to secure your home loan.
How to Calculate Your Loan to Value Ratio

Figuring out your loan to value ratio is actually pretty straightforward. You don't need to be a math whiz or fire up a complicated spreadsheet to get the number.
The good news is that it all comes down to one simple formula.
The LTV Formula:
Loan to Value Ratio = (Loan Amount / Appraised Property Value) x 100
This simple equation tells you—and your lender—what percentage of the home's total value you're borrowing. Let's walk through a real-world example so you can see exactly how it works.
Putting the Formula into Action
Let's say you've found the perfect home with a $400,000 price tag. You've saved up and are ready to put down $80,000. That means you'll need a mortgage for the rest.
Here's how we plug those numbers into the LTV formula:
-
Find Your Loan Amount:
- Purchase Price: $400,000
- Down Payment: $80,000
- Loan Amount Needed: $320,000 (That's just $400,000 – $80,000)
-
Use the Appraised Value: For this example, let's assume the official appraisal came in right at the purchase price: $400,000.
-
Calculate the LTV:
- ($320,000 Loan Amount / $400,000 Appraised Value) = 0.80
- 0.80 x 100 = 80% LTV
In this case, your LTV is 80%. This is a magic number for a lot of lenders, including us at Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage), because hitting this mark often means you can skip paying for Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI).
The Critical Role of Appraised Value
Here's a crucial detail that trips some people up: the "value" part of the LTV calculation isn't always the price you agree to pay.
You might offer $420,000 for a house, but if the independent appraiser says it’s only worth $410,000, the lender is going to use that lower number.
Lenders always use the lesser of the purchase price or the appraised value.
This is a safeguard for the lender. It prevents them from lending more money than the property is actually worth if something goes wrong. To get an accurate LTV, you have to know what determines a property's market value from a professional's perspective.
Calculating LTV for a Refinance
The same formula works for refinancing your mortgage, but the numbers you use are a bit different. Instead of a purchase price, you'll use your current mortgage balance and a fresh appraisal.
Imagine you owe $250,000 on your current mortgage. After some home improvements, a new appraisal shows your home is now worth $500,000.
- Current Loan Balance: $250,000
- New Appraised Value: $500,000
- LTV Calculation: ($250,000 / $500,000) x 100 = 50% LTV
Having an LTV this low shows you've built up a ton of equity. It puts you in a fantastic position to get great rates and terms on a new loan. Once you get the hang of this simple calculation, you’ll have a much better idea of how lenders will see your application.
Why Your LTV Is a Big Deal for Mortgage Approval
When a lender looks at your mortgage application, they're trying to figure out one main thing: risk. Your loan-to-value ratio gives them a crystal-clear picture of just how much risk they're taking on. A high LTV means you have less of your own money—less "skin in the game"—invested in the property. In their eyes, that can signal a higher chance you might default if times get tough.
This isn't just some abstract number on a form; it has real-world consequences. Metrics like LTV are exactly what lenders, including Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage), use to decide the terms of your loan. It directly affects your interest rate, dictates whether you'll be on the hook for mortgage insurance, and can ultimately make or break your approval.
Simply put, a lower LTV shows you're a serious, committed buyer, which makes your application look a whole lot stronger.
How LTV Directly Impacts Your Loan Terms
Think of your LTV like a volume dial for the cost of your mortgage. A small adjustment can dramatically change your monthly payment and how much you pay over the long haul.
Here are the biggest ways LTV shapes your home loan:
- Interest Rates: Lenders reward low-risk borrowers with better deals. Someone with an 80% LTV is seen as a much safer bet than a borrower with a 97% LTV. As a result, they'll often get a lower interest rate. Even a tiny rate drop can save you thousands upon thousands of dollars over the life of your mortgage.
- Mortgage Insurance Requirements: This is a big one. For most conventional loans, if your LTV is over 80%, you’ll have to pay for Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI). It’s an extra fee tacked onto your monthly payment that protects the lender—not you—if you can't pay.
- Loan Program Eligibility: Different loan programs have hard limits on LTV. If yours is too high, you might not even qualify for certain types of mortgages, which narrows your options considerably.
Your LTV ratio is more than a simple calculation. It’s a direct reflection of the lender’s risk. A lower LTV doesn't just boost your approval odds; it unlocks better terms that save you real money.
Comparing High vs. Low LTV Borrowers
Let's see how this works in the real world. Imagine two different buyers looking at the same home appraised for $350,000.
Borrower A: The Low LTV Applicant
This buyer puts down a solid 20%, which is $70,000.
- Loan Amount: $280,000
- LTV Ratio: ($280,000 / $350,000) = 80%
- The Outcome: This is the sweet spot. Borrower A will likely lock in a great interest rate and, crucially, won't have to pay a dime in PMI. Their strong equity position makes them a dream applicant for lenders.
Borrower B: The High LTV Applicant
This buyer can only manage a 5% down payment of $17,500.
- Loan Amount: $332,500
- LTV Ratio: ($332,500 / $350,000) = 95%
- The Outcome: Borrower B is almost guaranteed to be paying PMI every single month, adding a hefty cost to their payment. They might also get hit with a slightly higher interest rate because the lender sees them as a bigger risk.
While your LTV is a huge piece of the puzzle, remember that your credit score is right there with it. Knowing how to get all three credit reports free is a great first step to making sure your entire financial profile is as strong as it can be when you apply.
A Global Standard for Assessing Risk
The loan-to-value ratio isn’t just a local standard; it’s a key metric used by lenders worldwide to weigh mortgage risk. It always comes down to the loan amount versus the property's appraised value.
Historically, LTV standards have shifted with the housing market. Before the 2008 financial meltdown, some lenders got incredibly reckless, allowing LTVs to soar as high as 125%. We all know how that ended. In the aftermath, regulations clamped down hard, and lenders everywhere lowered their maximum LTVs to prevent another crisis, proving just how central this metric is to the stability of the entire financial system.
LTV Requirements for Different Mortgage Programs
Not all mortgages are created equal, and their loan-to-value requirements can be worlds apart. Getting a handle on these differences is the key to finding a loan that actually fits your financial reality. Each program has its own LTV limits, and that number directly impacts how much cash you’ll need to bring to the closing table.
Some loans are backed by the government to make homeownership more accessible, while others are built for borrowers with a stronger financial footing. Let's break down the common options to see what's possible for you.
This visual gives you a quick snapshot of how lenders see LTV from a risk perspective.
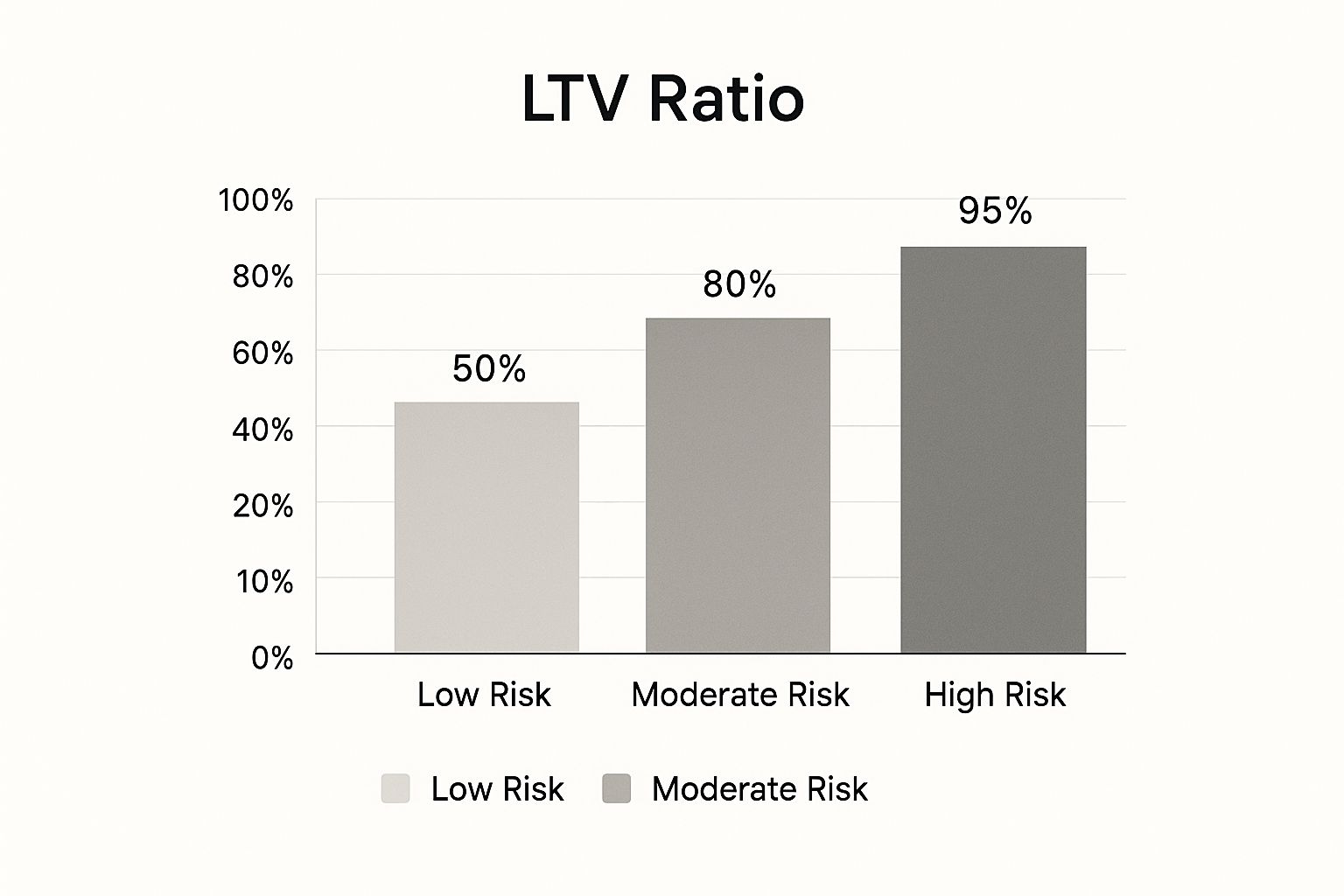
As you can see, a lower LTV is a lender’s best friend—it means less risk. A higher LTV, on the other hand, signals more risk, which usually means stricter requirements or extra costs like mortgage insurance.
Conventional Loans
Conventional loans are the workhorses of the mortgage world, but they also tend to play by the strictest rules. Most lenders want to see an LTV of 80% or lower. To hit that mark, you'll need a down payment of at least 20%, which is the magic number for avoiding Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI).
Can you get a conventional loan with less down? Absolutely. Some programs allow an LTV as high as 97% (meaning just a 3% down payment), but be prepared for that extra PMI payment every month. The logic is simple: more skin in the game from you means less risk for them.
FHA Loans
FHA loans, which are insured by the Federal Housing Administration, are a game-changer for many first-time homebuyers and people with imperfect credit. They are built to be flexible.
With an FHA loan, you can often get approved with an LTV as high as 96.5%. That works out to a down payment of just 3.5%, which is a much more achievable goal for many buyers. The trade-off is that all FHA loans come with mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), no matter how much you put down.
VA and USDA Loans
This is where things get really interesting for certain buyers. If you’re eligible, both VA loans (for veterans and active-duty service members) and USDA loans (for homes in designated rural areas) offer the incredible possibility of 100% financing.
That’s right—qualified buyers can get a mortgage with a 100% LTV, which means a $0 down payment. This single benefit removes one of the biggest hurdles to owning a home for countless deserving families.
These government-backed programs give lenders a guarantee, which lowers their risk and empowers them to offer terms you just can't find anywhere else.
Comparing LTV Limits and Down Payments by Loan Type
To make it easier to see how these programs stack up, here’s a quick comparison of their LTV and down payment requirements.
| Loan Program | Maximum LTV Ratio | Minimum Down Payment | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 97% (in some cases) | 3% (but 20% to avoid PMI) | PMI required for LTV over 80%. |
| FHA | 96.5% | 3.5% | Mortgage insurance is required for all loans. |
| VA | 100% | 0% | For eligible veterans and service members only. |
| USDA | 100% | 0% | For eligible borrowers in designated rural areas. |
| Non-QM | Varies widely | Varies widely | Flexible underwriting for unique financial situations. |
This table shows just how much your loan options can change based on the program. From 0% down with a VA loan to the standard 20% down for a conventional loan, the path to homeownership looks different for everyone.
Non-QM Loans
What about borrowers who don’t quite fit the standard mold? For the self-employed, real estate investors, or anyone with a unique financial story, Non-Qualified Mortgage (Non-QM) loans are a vital lifeline.
At Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage), we specialize in these kinds of flexible solutions. While the LTV requirements for Non-QM loans vary from person to person, they create a clear path to homeownership when other doors have closed.
Putting It All in Perspective
So, what does a "typical" LTV look like in the real world? On the whole, lenders prefer borrowers who have a solid amount of equity in their homes right from the start.
The LTV ratio is also front and center when you want to tap into your home's equity later on. You can learn more about how it works by checking out our guide on cash-out refinance requirements.
Practical Strategies to Lower Your LTV Ratio
Getting a lower LTV is one of the smartest moves you can make as a homebuyer. It makes your mortgage application look stronger, helps you land better interest rates, and is the key to avoiding expensive private mortgage insurance. While the obvious advice is just to "save more money," there are several real-world strategies you can actually use to beef up your down payment and bring that loan-to-value ratio down.
These approaches will give you a clear roadmap to improve your financial footing before you even apply for a loan.
Build a Dedicated Down payment Fund
The most direct and effective strategy is to simply increase your down payment. A bigger down payment shrinks the amount you need to borrow, which is the quickest way to lower your LTV. Don't just save aimlessly; create a dedicated plan.
Start by opening a separate, high-yield savings account just for your down payment. Then, automate your contributions with scheduled transfers from your checking account. This "set it and forget it" approach ensures you're consistently making progress.
Here are a few steps to speed up your savings:
- Create a Budget: Get a handle on your income and expenses. Find areas where you can cut back and redirect that cash straight into your down payment account.
- Set Clear Milestones: Break your big savings goal into smaller, monthly targets. It keeps you motivated and makes it easier to track your progress.
- Look for Extra Income: Think about a side hustle or some freelance work. If you dedicate all those extra earnings to your down payment fund, it can add up fast.
Explore Down Payment Assistance Programs
Many homebuyers have no idea that help is out there. Down payment assistance (DPA) programs are offered by state and local governments to make homeownership a reality for more people. These programs can provide grants or low-interest loans to help you cover the down payment and closing costs.
This funding can give your upfront cash a serious boost, which directly lowers your LTV. Here at Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage), our loan officers are experts at helping you find and apply for DPA programs you might qualify for in your area.
A lower LTV doesn't just happen—it's the result of a deliberate financial strategy. By combining disciplined saving with smart resourcefulness, you can put yourself in a much stronger borrowing position.
Document and Use Gift Funds
If you’re lucky enough to get some financial help from family, these "gift funds" are a fantastic way to lower your LTV. Lenders are perfectly fine with accepting gift funds, but they have to see specific documentation to prove the money isn't a loan in disguise.
You’ll need a signed gift letter from the person giving you the money. This letter must clearly state that the funds are a gift with no expectation of repayment. You will also have to show bank statements tracing the money from the donor's account into yours. Getting this paperwork right is a crucial step for a smooth approval.
Negotiate Seller Concessions
When you’re in the process of buying a home, you can negotiate for the seller to pay for some of your closing costs. These are called seller concessions. While this doesn’t directly reduce your LTV, it frees up the cash you would have spent on those costs.
You can then take that extra cash and apply it directly to your down payment. This effectively increases your contribution and lowers your LTV. A good real estate agent can be a huge help in negotiating these terms. Lowering your LTV is just one piece of the puzzle; for more ideas, check out our guide on how to lower your mortgage payment to see the full picture.
Navigating Your Home Loan with an Expert Partner

Understanding your loan-to-value ratio is a great first step, but it’s just one piece of the much bigger homebuying puzzle. The numbers tell a story, but what you really need is a trusted partner who can interpret that story and steer you toward the best possible outcome.
This is exactly where working with a dedicated mortgage expert changes the game. It’s about partnering with a team that looks at the complete picture of your financial life, not just one number on a page.
At Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage), we believe in arming homebuyers with clear, straightforward knowledge. We don't just shuffle applications around; we build personalized solutions that actually fit your unique situation.
Your Guide Through the Mortgage Maze
Whether you’re sitting on a fantastic low LTV or need some practical advice on how to improve it, our team is here to help you get to the finish line. We get it—every borrower’s journey is different. That’s why we’re committed to digging in and finding the right loan program for your specific goals.
Our one-on-one support means you never feel lost or left in the dark. We break down the complicated stuff and lay out your options clearly, so you can make decisions with real confidence. Let's be honest, navigating the world of home loans can feel overwhelming, but you absolutely don't have to go it alone.
The right mortgage partner does more than just calculate your loan to value ratio; they help you build a financial strategy that turns your dream of homeownership into a reality.
Let's connect. The specialists at RAC Mortgage are ready to explore your home loan options with you. We can help you confidently take that next step toward your new front door. Your homeownership goals are within reach, and we have the expertise to get you there.
LTV Questions We Hear All The Time
Even after you've got the basics down, it's totally normal to have a few more questions pop up. The loan-to-value ratio has a lot of moving parts, and how they apply to your specific situation is what really matters on your mortgage journey.
We’ve pulled together some of the most common questions homebuyers ask us. Let's get you some clear, direct answers so you can move forward without any nagging uncertainties.
How Does My Credit Score Affect LTV?
Think of your credit score and LTV as a team. They're two of the biggest factors a lender looks at, and they absolutely influence each other. A high credit score tells a lender like Residential Acceptance Corporation (RAC Mortgage) that you're a reliable borrower.
When a lender sees less risk, they're often willing to be more flexible on LTV. For instance, a buyer with a 760 credit score might sail through an approval for a conventional loan with a 97% LTV. On the flip side, someone with a 640 score might need to bring a bigger down payment (creating a lower LTV) to get approved for that same loan. A strong credit history can open the door to higher LTV options and, usually, better interest rates.
What's a Combined Loan-to-Value (CLTV) Ratio?
The Combined Loan-to-Value (CLTV) ratio comes into play when you have more than one loan stacked on a single property. This could be your main mortgage plus a second loan, like a home equity line of credit (HELOC) or a home equity loan.
Calculating it is pretty straightforward:
(Total of All Loan Balances / Appraised Property Value) x 100 = CLTV
Let's say your home is valued at $500,000. You have a primary mortgage of $350,000 and you just took out a $50,000 HELOC. Your total debt on the property is now $400,000. That makes your CLTV 80% ($400,000 divided by $500,000). Lenders use this number to gauge their total risk exposure if you apply for another loan or a refinance.
Can I Refinance with a High LTV?
Refinancing when you have a high LTV is tricky, but it's not always a dead end. Most traditional refinance programs want to see your LTV at 80% or lower to give you the best rates and terms. But don't lose hope—some government-backed programs were created specifically to help homeowners in this exact spot.
It's also interesting to see that LTV isn't just a local lender rule; it's a tool used worldwide to keep housing markets stable. Research shows that when countries put maximum LTV caps in place, it cuts down on high-risk lending. These limits, often capping loans at 80-90% of a home's value, stop borrowers from getting in over their heads. You can dive deeper into these global effects by checking out the global lending from the IMF's analysis.
For homeowners staring down a high LTV, the best move is to talk to a lender who knows the landscape. An expert can see if you qualify for a specialized program that fits your needs.
Your path to owning a home is one-of-a-kind, and having a pro in your corner changes everything. At Residential Acceptance Corporation, we give you the personalized guidance to understand every part of your mortgage, from LTV to the closing table. Get in touch with us today to start your application and take that next step.

